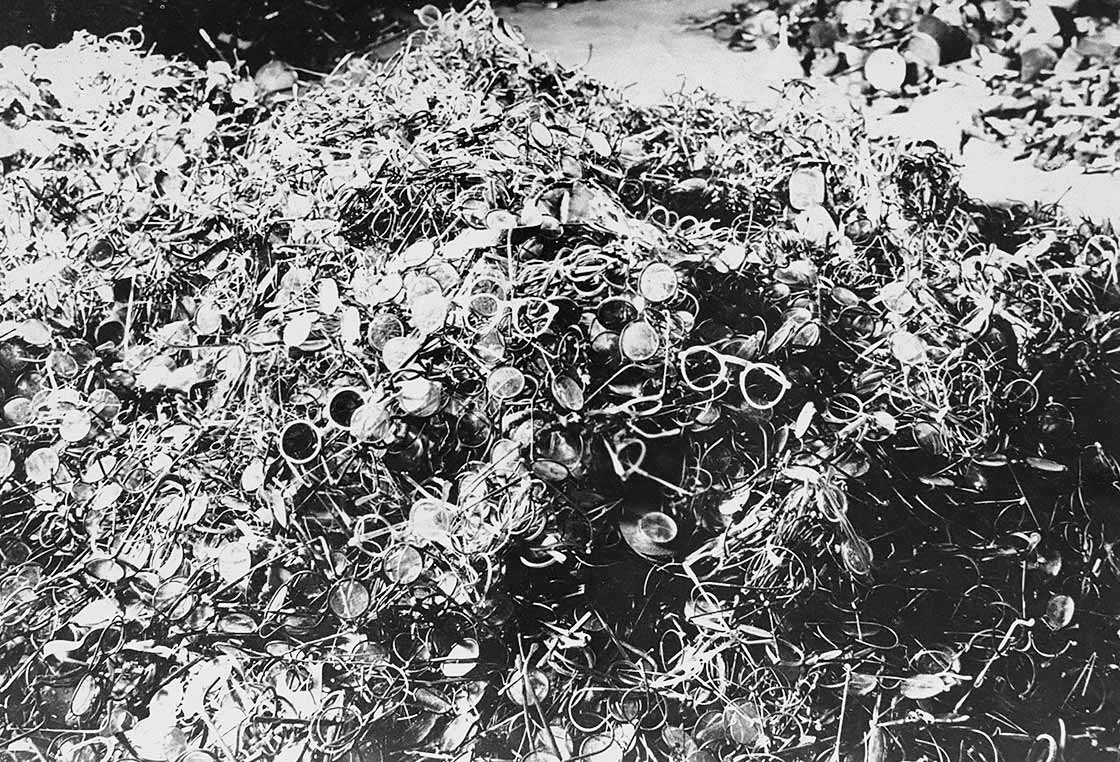
Above: A mountain of eye glasses in Auschwitz. Bundesarchiv, Bild 183-R69919 / CC-BY-SA 3.0 [CC BY-SA 3.0 DE]
If we are to hope to understand the often violent world in which we live, we cannot confine our attention to the great impersonal forces, natural and man-made, which act upon us. The goals and motives that guide human action must be looked at in the light of all that we know and understand; their roots and growth, their essence, and above all their validity, must be critically examined with every intellectual resource that we have.
Isaiah Berlin’s last book was inspired by the German philosopher Immanuel Kant, who, in one of the great one-liners of philosophy, summarized the history of civilization thusly: “Out of the crooked timber of humanity no straight thing was ever made.” The grain of the past, Kant and Berlin understood, is twisted and full of knots. Rarely do historical events of any magnitude or import match the linear progression of cardboard textbook histories. Instead, the past is quirky and nonlinear. So it is with Auschwitz, whose crooked history led it to become the deadliest site in the worst genocide in modern history.
From Euthanasia to Mass Murder
Long before prisoners were herded into gas chambers and killed with Zyklon-B or carbon monoxide gas, the Nazis had developed a program of systematic and secret murder of targeted peoples. It began with the sterilization programs of the early 1930s, evolved into the euthanasia programs of the late 1930s, and with this experience the Nazis were able to implement mass murder in the extermination camps from 1941–1945. As shocking as gassing masses of prisoners in a chamber seems, as psychologists know it is actually easy to get people to do almost anything when the steps leading to it are small and incremental. After murdering tens of thousands of “inferior” Germans, the idea of attempting to annihilate the Jewish people did not appear unimaginable. Once targeted peoples have been demonized, excluded, expelled, sterilized, deported, beaten, tortured, and euthanized, the step to mass murder is a small one.
Sterilization laws were passed in late 1933. Within a year 32,268 people were sterilized. In 1935, the figure jumped to 73,174, with official reasons given including feeblemindedness, schizophrenia, epilepsy, manic-depressive psychosis, alcoholism, deafness, blindness, and even malformations. So-called sex offenders were simply castrated, no fewer than 2,300 in the first decade of the program.

Order an autographed copy from Shop Skeptic, while supplies last. In the Comments field during checkout, you may specify to whom you would like it personalized.
In 1935, Hitler told the leading Reich physician, Gerhard Wagner, that when the war began he wanted to make the shift from sterilization to euthanasia. True to his word, in the summer of 1939 the Nazis began killing physically handicapped children, then quickly moved on to mentally handicapped children, and soon after to adults with either handicap. The murders were initially committed through large doses of “normal” medication given in tablet or liquid form, so as to look like an accident (families were notified of the death). If the patients resisted, injections were used. When the numbers chosen for death became cumbersomely large, however, the operations had to be moved into special killing wards instead of isolated units.
The process became so extensive that the Germans had to expand their operation by taking over an office complex set up at a stolen Jewish villa in Berlin, located at Tiergarten Strasse #4. Thus, the program became known as Operation T4, or just T4, the “Reich Work Group of Sanatoriums and Nursing Homes”. T4 doctors arbitrarily decided who would live and who would die with, among others, economic status one of the common criteria—those unable to work or only able to perform “routine” work could be put to death. Historians estimate that approximately 5,000 children and 70,000 adults were murdered in the euthanasia program prior to August, 1941.

Figure 1. Hartheim Castle, 1940, a site of a T4 “euthanasia” killing center. Smoke from the small crematorium constructed inside for burning the bodies of victims can be seen in the background. From: United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, Washington, DC.
As the numbers increased so too did the complications of murder on such a scale. Mass murder requires a mass murder process, and medication and injections did not suffice. The T4 physicians were aware of the fact that some accidental deaths and suicides were the result of gas from an automobile engine or a leaking stove. According to Dr. Karl Brandt, he and Hitler discussed the various techniques and decided upon gas as “the more humane way.” The T4 administrators set up six killing centers; the first established at an old jail building in the city of Brandenburg. Sometime between December, 1939, and January, 1940, a two-day series of gassing experiments was conducted and deemed successful. Thereafter five more killing centers were established, including one each at Grafeneck in Württemberg, Hartheim near Linz, Sonnenstein in Saxony, Bernburg in the Prussian province of Saxony, and Hadamar in Hessen. The gas chambers were disguised as showers, the “handicapped” patients herded in, and the gas administered. One observer, Maximilian Friedrich Lindner, recalled the process at Hadamar (Friedlander, 1995, 97):
Did I ever watch a gassing? Dear God, unfortunately, yes. And it was all due to my curiosity….Downstairs on the left was a short pathway, and there I looked through the window….In the chamber there were patients, naked people, some semi-collapsed, others with their mouths terribly wide open, their chests heaving. I saw that, I have never seen anything more gruesome. I turned away, went up the steps, upstairs was a toilet. I vomited everything I had eaten. This pursued me days on end….
The gas was ventilated from the chamber with fans, the bodies were disentangled and removed from the room, the corpses marked with an “X” on their back were looted for gold in their teeth, then cremated. The entire process—from arrival at the killing center to cremation—took less than 24 hours, not unlike what was soon implemented in the larger camps in the East. Henry Friedlander, who traced this evolutionary process, concluded (284): “The success of the euthanasia policy convinced the Nazi leadership that mass murder was technically feasible, that ordinary men and women were willing to kill large numbers of innocent human beings, and that the bureaucracy would cooperate in such an unprecedented enterprise.”
In the T4 killing centers we see all the components of the extermination camps like Auschwitz. Through time the Nazi bureaucracy evolved along with the T4 killing centers, setting the stage for the conversion of concentration and work camps into extermination camps. By 1941–1942, this was just another incremental step in the contingently evolving system that became the Final Solution.
This contingent history also helps us understand another mystery—the order from Hitler to exterminate the Jews. In our opinion, one of the reasons there exists no written order from Hitler is because he once authorized in writing the euthanasia of handicapped patients and this came back to haunt him. Furthermore, we know that as a general principle Hitler always tried not to sign orders himself. There is no order by Hitler, for example, to start the war. Herein lies the key to understanding the contingent evolution of the extermination camps—they evolved out of concentration camps and work camps, utilizing techniques for mass murder developed for the euthanasia program, disguised to maximize secrecy and security.
The Contingent History of Auschwitz
On April 21, 1990, David Irving addressed a large audience at the Löwenbräu Hall in Munich, Germany, proclaiming in his inimitable style of self-assured truth-telling: “By now we know, and I am sure I don’t need to point this out as anything more than an aside, that there were never any gas chambers in Auschwitz.” But are there not extant gas chambers still there at the camp for everyone to see? Yes, Irving admits, but “we believe that, just as the gas chambers which the Americans put up here in Dachau [outside Munich] in the first few days after the war were fakes, those gas chamber facilities which tourists can now sightsee in Auschwitz were set up by Polish authorities after the Second World War.” Why? Irving completed the conspiracy theory: “The German taxpayers have had to shell out no less than sixteen billion Deutschmarks as a penalty for Auschwitz for a fake” (cited on Irving’s web page: fpp.co.uk).
Holocaust deniers assume that because historians have determined that Auschwitz ended up being an extermination camp that it must have been originally designed to be an extermination camp. Since the layout, design, and function of Auschwitz does not match the expectations one might have for a perfectly designed extermination camp, deniers then argue that it was not an extermination camp at all. This is a flawed argument because historical outcomes rarely match historical intentions. In particular, it is a flawed argument because Auschwitz was not originally designed to be an extermination camp.
The architectural historian Robert-Jan Van Pelt, in a brilliant essay entitled “A Site in Search of a Mission,” has demonstrated through a chronology of blueprints and architectural designs of Auschwitz, that modern myths about the camp have erased the historical contingencies of its origin and development (1994, 93):
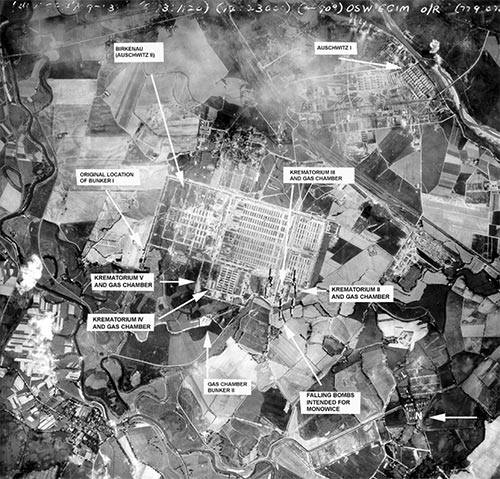

Figure 2. Auschwitz-Birkenau photographed from 30,000 feet by allied bombers on August 25, 1944 on on bombing run of the nearby IG Farben industrial plant at Monowice (note the falling bombs near the center of the photograph).
Banished from the world of description, analysis, and conclusion, Auschwitz has become a myth in which the assumed universality of its impact obscures the contingencies of its beginning. I use the word myth in the sense that Barthes gave to it in his essay “Myth Today.” Mythification, he argued, occurs when language empties a narrative of its historical contingency to fill it with an unchanging nature. “In passing from history to nature, myth acts economically: it abolishes the complexity of human acts, it gives them simplicity of essences.” The result is an account of “blissful clarity” in which there are no contradictions because statements of fact are interpreted as explanations; “things appear to mean something by themselves.” Few events can rival the mythic power of “Auschwitz.”

Figure 3. Aerial photograph of Crematoria II & III of Auschwitz-Birkenau (right of photograph). The shadows of the Zyklon-B gas induction vents can be seen on the top of the subterranean gas chambers (perpendicular to the crematorium building and noted in the photo captions).
In his essay, and even more poignantly in his 1996 book co-authored with Deborah Dwork, Auschwitz: 1270 to the Present, Van Pelt unravels the contingencies that constructed the necessity that became the Auschwitz we have come to know today. The problem is that we are trying to understand the early stages of Auschwitz by what now remains. The original intention of Auschwitz, however, was quite different. “Auschwitz was not preordained to become the major site of the Holocaust. It acquired that role almost by accident, and even the fact that it became a site of mass murder at all was due more to the failure to achieve one goal than to the ambition to realize another” (1994, 94). The focus on the final stage of Auschwitz as a killing machine has prevented us from understanding its contingent history, as well as how anyone could commit such a crime. Understood in historical context, however, we come to understand how Auschwitz and its operators evolved to assume the roles of mass murderers, as Van Pelt and Dwork so eloquently observe (1996, 11):

Figure 4. Ground photograph of Crematoria II showing the Zyklon-B gas induction vents (behind and to the right of the train smoke stack) that cast the shadows seen in the aerial photograph in Figure 3.
This almost comfortable demonization relegates the camp and the events that transpired there to the realm of myth, distancing us from all too concrete historical reality, suppressing the local, regional, and national context of the greatest catastrophe western civilization both permitted and endured, and obscuring the responsibility of the thousands of individuals who enacted this atrocity step by step. None of them was born to be a mass murderer, or an accomplice to mass murder. Each of them inched his way to iniquity.
Auschwitz, it seems, was to be a district capital, a center of mass industry, and a model city that would project the image of an ideal future city for the Thousand Year Reich. The Nazis believed that Poland was rightfully theirs and therefore they were “liberating” it. In an SS handbook entitled The Struggle for the German Eastern Border, SS men were told: “The German East was for centuries the German people’s space of destiny. It will remain so for the following centuries.” Concentration camps were originally designed as instruments of terror to control resistance to the Nazi Party (Dachau is the classic case), but in time as they evolved, they furnished labor for productive work, especially after 1939. (Before the war, the free labor of the camps would have competed with German businesses and thus increased unemployment, which went against Nazi policy.) When the war began, however, the camps took on two new functions: a source of labor and the housing of prisoners of war. And, with much of German productive labor on the fighting line, these two new functions blended into one, with prisoners providing the free labor.

Figure 5a. The remains of Crematoria II of Auschwitz-Birkenau taken by the authors: the undressing room. Note the stairs down into the subterranean structure at the rear of the structure at the top of the photograph.
In 1940, Himmler began to make plans for the future of Auschwitz. The industrial giant IG Farben would have a plant in Auschwitz, all Jews and Poles would be removed from the region, and Auschwitz itself would become “a paradigm of the settlement in the East” (Van Pelt and Dwork, 158). Within two months, a master architectural plan was completed for the reconstruction and enlargement of the camp, that included an SS Garden City and a center for agricultural experimentation. Nestled at the confluence of three major rivers, Auschwitz was to be the model Aryan city. Van Pelt and Dwork detail this evolution in blueprints and plans, including the first master plan for the expansion of Auschwitz, the location of the IG Farben industrial area, the Nazi Party headquarters, and, of course, the concentration/labor camp. The plans are also in keeping with Nazi architectural aesthetics as envisioned by Hitler and his chief architects Paul Troost and Albert Speer.

Figure 5b. A possible hole through which the Zyklon-B gas was introduced into the subterranean gas chamber, on top of which was the induction vent seen in Figures 3 & 4.
These plans changed on Sunday, June 22, 1941, when the Nazis invaded the Soviet Union. Contingencies once again altered future necessities, and the crooked timber of Auschwitz took another twisted turn. With the initial successes of the Wehrmacht and the Luftwaffe, Russian prisoners of war came pouring into Auschwitz, suddenly transforming the camp into an instrument of war. Conditions were brutal and thousands of Russians died monthly from disease and starvation: in October, November, and December, 1941, 1,255, 3,726, and 1,912 died, respectively. Barracks were hastily thrown up to house the POWs, and new crematoria had to be added to dispose of the bodies. The model-city-turned-POW-camp was, de facto, rapidly on its way to becoming an extermination camp.

Figure 5c. The remains of the crematoria after the entire structure was destroyed by the Nazis shortly before the camp was liberated in January 1945.
After the Russian armies began to hold the line against the Germans and it became clear that Operation Barbarossa—the German invasion of the Soviet Union—was going to become a protracted operation, Auschwitz was further expanded to house up to 100,000 prisoners, primarily for labor (German laborers were now being ground up in the German war machine and the concern for unemployment was no longer an issue). After Stalingrad and the turning of the tide in the East, the supply of free Russian labor began to dry up. Himmler needed a replacement and he found it in the Jews. The evolution of Auschwitz toward its final end as an extermination camp now took a dramatic leap.
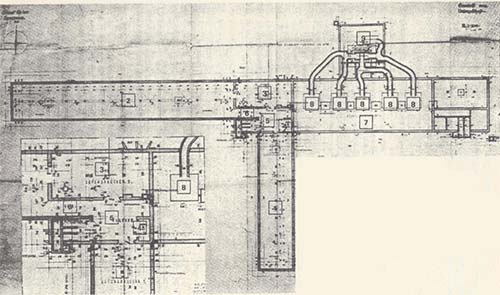
Figure 5d. Blueprint of Crematoria II: the left long rectangular structure is the subterranean undressing room; the perpendicular rectangular structure is the subterranean gas chamber.
At the Wannsee Conference where plans for the Final Solution were coordinated, SS-Obergruppenfuhrer Reinhard Heydrich declared that “Under appropriate direction the Jews are to be utilized for work in the East in an expedient manner in the course of the final solution. In large (labor) columns, with the sexes separated, Jews capable of work will be moved into these areas as they build roads.” Six days later, Himmler sent the following telegram to the Inspector of Concentration Camps, Richard Glücks: “As no Russian prisoners of war can be expected in the near future, I am sending to the camps a large number of Jews who have emigrated from Germany. Will you therefore make preparation to receive within the next four weeks 100,000 Jews and up to 50,000 Jewesses in the concentration camps. The concentration camps will be faced with great economic tasks in the coming weeks” (Van Pelt, 1994, 148–149).

Figure 5e. The remains of the entire Crematoria II structure today (with tourists visiting the site) courtesy of the Holocaust History Project.
Indeed they were. Three weeks later, the first transport of Jews arrived, whereupon the young and healthy were put to work and the old and infirm were gassed and cremated. When this procedure became cumbersome, given the confines of the camp’s original design, it was moved three kilometers away, from Auschwitz I to Auschwitz II, better known as Auschwitz-Birkenau, where new crematoria were constructed, and the killing escalated as the war intensified. Yet all the while, says Van Pelt, “the extermination of the Jews was meant to be a transient phenomenon in the history of the camp.” Plans were continued to convert the camp yet again after the war, but “that other future never materialized. Thus the name Auschwitz became synonymous with the Holocaust, and not with Himmler’s model town” (150–151).

Figure 6. This photograph shows the burning of bodies in an open pit after gassing (sometimes necessary when the crematoria broke down or couldn’t keep up with the killings). A Sonderkommando (Jews forced to work for the Nazis) at Auschwitz-Birkenau took them secretly. Alter Fajnzylberg, another Sonkerkommando, described what happened: “On the day on which the pictures were taken we allocated tasks. Some of us were to guard the person taking the pictures. At last the moment came. We all gathered at the western entrance leading from the outside to the gas chamber of Crematorium V: we could not see any SS men in the watch-tower overlooking the door from above the barbed wire, nor near the place where the pictures were to be taken. Alex, the Greek Jew, quickly took out his camera, pointed it toward a heap of burning bodies, and pressed the shutter. This is why the photograph shows prisoners from the Sonderkommando working at the heap.” (In: Swiebock, T. 1993. Auschwitz: A History in Photographs. Bloomington: Indiana University Press)
Proving Gas Chambers and Crematoria Were Used for Genocide
Holocaust deniers claim that gas chambers were used strictly for delousing clothing and blankets, and crematoria were used to dispose of the bodies of those who died of “natural” causes in the camps. How can we distinguish between gas chambers used for delousing and gas chambers used for genocide? How can we prove that the bodies disposed of in crematoria were murdered and had not just died of so-called “natural” causes like disease, starvation, and overwork?
To find out, we went to Europe to conduct research at the camps, in particular Mauthausen, Majdanek, Treblinka, Sobibor, Dachau, Auschwitz, and Auschwitz-Birkenau, to see for ourselves just what evidence there is at the camps. But before examining the evidence we gathered at the camps, consider in general how we might prove through a convergence of evidence from various sources that the Nazis used gas chambers and crematoria for mass murder:
- Zyklon-B Gas Traces — On the walls of the gas chambers at several camps are traces of the gas Zyklon-B, used to exterminate large numbers of prisoners.
- Eyewitness testimony — Survivor testimonies, Jewish Sonderkommando diaries, and confessions of guards and commandants.
- Written documents — Orders for Zyklon-B (the trade name of hydrocyanic acid gas), architectural blueprints, and orders for building materials for gas chambers and crematoria.
- Ground Photographs — Not only of the camps, but also the secret photos taken of bodies burning, subsequently smuggled out of Auschwitz.
- Aerial Photographs — Taken of Auschwitz showing prisoners being moved toward the gas chamber/crematorium complexes, matching those of ground photographs corroborating the structure of the gas chambers and crematoria.
- The Camps — The extant ruins of the camps themselves, when examined in light of the above sources of evidence, reveal the homicidal use of both gas chambers and crematoria for the express purpose of exterminating large numbers of prisoners.
In all there were six extermination camps involved in the Final Solution, resulting in a total of approximately 3,062,000 killed (Friedlander, 1995, 287):
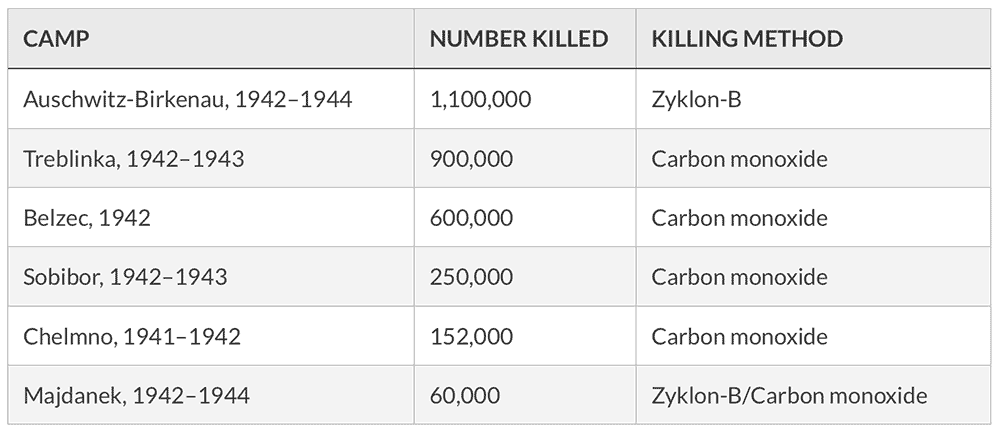
What the Nazis learned in the T4 program, along with subterfuge and secrecy and the methods of mass murder, is that the public would not tolerate such activities on German soil. Thus, these six camps were located in the East, far from the watchful eyes of the German public and press. But the evidence to convict the murderers has not escaped history. ![]()
About the Authors
Alex Grobman is an historian with an MA and Ph.D. in contemporary Jewish history from The Hebrew University in Jerusalem. He is president of the Institute for Contemporary Jewish Life, a think tank dealing with historical and contemporary issues affecting the Jewish community. He is a contributing editor for Together, a publication of the American Gathering of Jewish Holocaust Survivors and Their Descendants. He is a member of the academic board of the David S. Wyman Institute for Holocaust Studies and a contributor to the Encyclopedia Judaica and the Partisan website. He reviews books for the Jewish Voice and Opinion.
Michael Shermer is the Publisher of Skeptic magazine, a Presidential Fellow at Chapman University, and the host of the Science Salon podcast. For 18 years he was a monthly columnist for Scientific American. He is the author of Why People Believe Weird Things, The Science of Good and Evil, Why Darwin Matters, The Believing Brain, The Moral Arc, and Heavens on Earth. His next book is Giving the Devil His Due: Reflections of a Scientific Humanist. Follow him on Twitter @michaelshermer
References
- Friedlander, Henry. 1995. Origins of Nazi Genocide: From Euthanasia to the Final Solution. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. See also: Kogon, E., H. Langein, and A. Rückerl (eds.). 1993. Nazi Mass Murder: A Documentary History of the Use of Poison Gas. New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Van Pelt, Robert-Jan. 1994. “A Site in Search of a Mission.” In Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp. Y. Gutman and M. Berenbaum (eds). Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
- Dwork, Deborah and Robert-Jan Van Pelt. 1996. Auschwitz: 1270 to the Present. New York: W. W. Norton.
This article was published on January 26, 2020.















Some of the comments here are astounding. There are too many horrible people in the world.
Anyone that studies the “holocaust” objectively for 5 minutes knows that it’s a lie
It’s not practical to use louse disinfestant dumping it through holes in the ceiling as alleged, much better, safer methods including using the blowing-air-circulation heating/ opening apparatus used in the delousing chambers.
Also not logistical to cremate thousands per day in crematoria: where was the fuel, it takes an hour per body, etc.
The gas chambers was atrocity propaganda along with the 6,000,000. Many died of typhus epidemics, hence the shaved heads, “selections,” crematoria and showers before entering a camp.
; lt’s more-than-obvious that the “Holocaust” is another, in a long, continuing line, of “Doomsday Cults”. More screaming, self-important, knuckle-heads, wearing togas, sandals, various sloganeering buttons, waving butterfly nets, wearing Napoleon hats, waving, poorly, hand-lettered signs extolling “The End Is Nigh”!
The latest version is Greta Thunberg, and the global-warming doomsday cult.
Hummm, Good punk-rock group name.
One must wonder what the Rabbis had in their diplomatic-pouches, what they knew, and when they knew it, e.g., 14 April 1932, the release date of the motion-picture titled “Symphony of Six Million”. This is an interesting bit of presence. Interestingly the photographs of prisoners “liberated” from the various camps from world war II, resemble the prisoners “liberated” from the various camps from the American Civil War.
Just answering questions.
What I’m seeing concerning the events of world war II, is another “doomsday cult” involving human sacrifice, and the denial of the common courtesy of grief process for the “survivors”, their families, and friends. More’s the pity of grief process denied.
What we have to do is constantly remind ourselves, our children, and our grandchildren, how we allow “others” to control our lives. As long as we teach our children to be blindly obedient to authority, or to be blindly patriotic, there will be more wars, atrocities and genocides. The children of the world have to be taught not to be blind followers of anyone.
This holocaust was nothing unique. Look up the Mongol occupation of Russia, the Spanish conquest of Mexico, or the things done by the Americans in the 19th century to American Indians. Humans have been doing this sort of thing for ages. The main motivation for deniers is they just get sick and tired of hearing about something that happened three generations ago and has no relavance to their own lives. Yes, it was horrible. And, yes, given human nature, it could and probably will happen again, but it has nothing to do with todays issues and should be forgotten except by historans.
How many Vietnamese did the US kill? How many Iraqis? How was the German policy any worse than building nuclear bombs? A nation with THOUSANDS of nukes ready launch on order to destroy the earth has no right to feel smug about anything Germany did in WW2.
I agree the holocaust did happen, and I would rather it had not. But I get tired of constantly being reminded about it. It should be forgotten. Constantly harping on it does nothing to prevent the next time from happening.
Great article, reading it I hope nothing like that
happens here. Kids in cages, hate marches; we must
be vigilant of the divisions in this country and try
to prevent cult like hate turn into government policy.
I want to ask the deniers if the Germans had built the gas chambers for innocent purposes like delousing, why did they feel the need to blow them up before they abandoned the camp? Seems like consciousness of guilt over something, no? “The Russians are at the gates! Quick, blow up the delousing facility!” Seems unnecessary unless they were trying to hide what they’d been up to.
In the last months of World War II my father was a Royal Artillery major serving as a staff officer with Field-Marshal Montgomery’s 21st Army Group. He was one of the staff officers who first entered the extermination camps. After the war, he would never under any circumstances talk to us about this experience. But he had no tolerance for Holocaust deniers, and he would have been horrified to encounter neo-Nazis expounding their poisonous lies.
It would be interesting to read an article on the history of
Anti- semitism in Germany.
People often ask how this could happen in such a sophisticated culture. They need to know that medieval Germany was a breeding ground for attitudes that eventually led to the Final Solution.
Excellent writing on the history of The Final Solution.
Another indication of how we humans come up with outrageous explanations, via conspiracy techniques, to explain something that we can’t wrap our little minds around. Obviously, some of us think, this must be another government secrecy “they” are hiding from us. So the story grows and gets more convoluted every time it is told to someone else.
Excellent history, but profoundly disturbing. Thank you both for your research & writing.
The late Saul Green told me that he and a few other GIs were the first Americans to happen upon Auschwitz, unaware of what it was, which must have been a nightmare for them. He took some photos with his Brownie camera.