free will

Shermer and Wilkinson discuss: • evolution: random chance or guided process? • selfishness and altruism • aggression and cooperation • inner demons and better angels • love and lust • free will and determinism • the good life and the good society • empirical truths, mythic truths, religious truths, pragmatic truths • Is there a cosmic courthouse where evil will be corrected in the next life? • theodicy and the problem of evil: Why do bad things happen to good…

Shermer and Klaas discuss: contingency and necessity/convergence • chance and randomness • complexity and chaos theory • Jorge Luis Borges “The Garden of Forking Paths” • self-organized criticality • limits of probability • frequency- vs. belief-type probability • ceteris paribus, or “all else being equal” • economic forecasting • Holy Grail of Causality • Hard Problem of Social Research • Special Order 191 and the turning point of the Civil War • Hitler, Nazi rise to power in Germany, World…

Shermer and Goff discuss: • living in a computer simulation • the universe itself as a conscious mind • cosmic purpose • fine-tuning • free will • consciousness (the ground of all being?) • morality and the Is-Ought Fallacy • What is my purpose in life? • religious vs. secular answers to the purpose question • awe and how to be spiritual but not religious.

Shermer and Sapolsky discuss: free will, determinism, compatibilism, libertarian free will • Christian List’s 3 related capacities for free will • how what people believe about free will and determinism influences their behaviors • the three horsemen of determinism: (1) reductionism (2) predetermination; (3) epiphenomenalism • dualism • punishment • retributive vs. restorative justice •Is the self an illusion? • game theory evolution of punishment • luck • and meaning (or lack thereof).

Preeminent philosopher and cognitive scientist, Daniel Dennett has spent his career considering the thorniest, most fundamental mysteries of the mind. Do we have free will? What is consciousness and how did it come about? What distinguishes human minds from the minds of animals? Dennett’s answers have profoundly shaped our age of philosophical thought. In his autobiographical I’ve Been Thinking, he reflects on his amazing career and lifelong scientific fascinations.

Shermer and Kaku discuss: AI, GPT, sentience/consciousness, the end of humanity • decoherence • Uncertainty Principle • multiverse, parallel universes, and Many Worlds hypothesis • Einstein • the evolution of the computer • the origin of life • climate change solutions • feeding 10 billion people • gene editing • curing cancer • immortality • simulating the universe • UAPs and UFOs • chaos theory and indeterminism • Are we living in a simulation? • Is there a God? •…

Shermer and Sheldon discuss: definitions of free will, determinism, compatibilism, libertarian free will • dualism • reductionism, materialism, predetermination, and epiphenomenalism • Christian List’s three capacities for free will • AI, Star Trek’s Data, sentience and consciousness, ChatGPT, GPT-4 • how what people believe about free will and determinism influences their behaviors • the case for hard determinism • brain injuries, tumors, addictions, and other “determiners” of behavior • emergence • symbolic self • System 1 vs. System 2 thinking • Experiencing Self vs.…

In their debate on free will, Doyle and Whittenberger present, explain, and defend contrasting, inconsistent, and in some ways contradictory models of human decision making. Whittenberger believes that the free will model is far inferior to the hard determinism model in so many ways, including conceptual clarity, the reasonableness of premises, and evidential support. Read Whittenberger’s response to Doyle.

My recent Skeptic article, “Free Will Is Real,” has prompted a response from Gary Whittenberger, who has previously written a standalone article for Skeptic in which he takes a stance against free will.1, 2, 3 Whittenberger’s response to me consists of several distinct points. A few of them are misunderstandings of my position. And a […]

The debate on free will vs. determinism has continued unabated for roughly 2500 years and seems to have become more prolific in the last ten years. Recently, Stuart T. Doyle presented his view in support of free will, the libertarian version. I strongly encourage the reader to study that article first. My intention here, however, […]
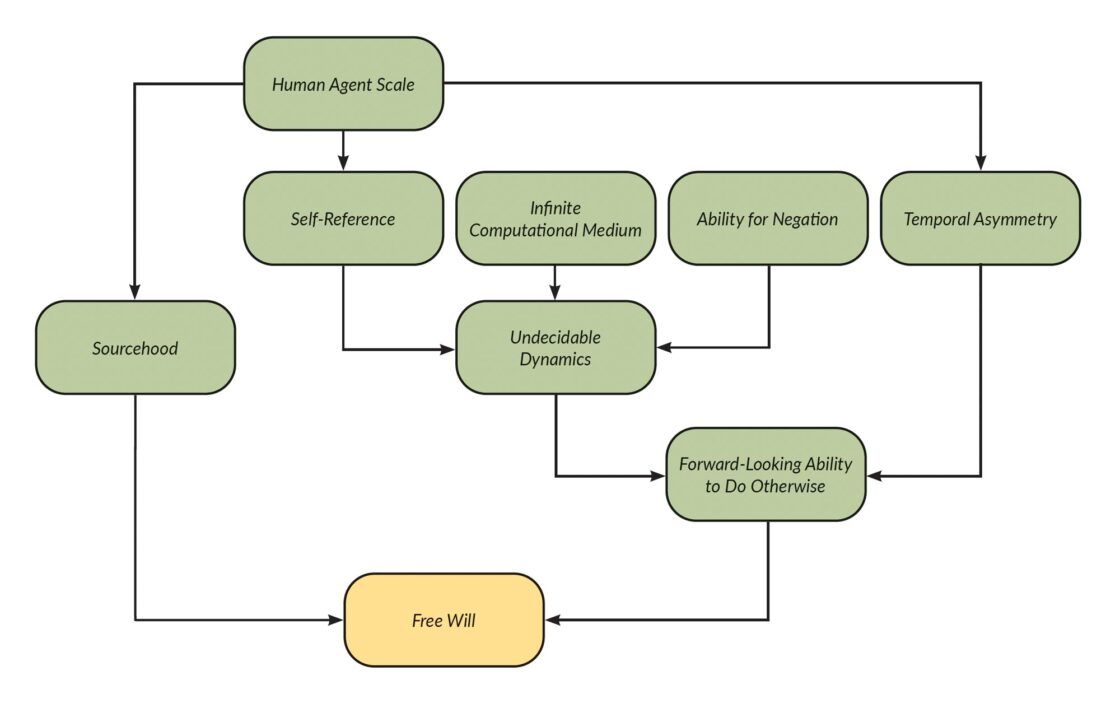
Are we really free? The question “Could I have done otherwise?” is central to the issue of free will. But because choices are forward-looking, at the time of choice there is not yet any action to do otherwise. The question makes more sense when aimed at the future: “Can I do something fundamentally unpredictable?” The answer is yes! Humans possess properties that make us capable of undecidable dynamics, meaning we are fundamentally unpredictable, and so we do have free will.

The philosophical problem of free will and determinism—how can humans have any sort of volition in a world determined by the laws of nature?—has troubled thinkers since the time of the ancient Greeks, and here in the 21st century there is still no consensus among thinkers on a solution to the problem. Can science help? Is there some way to test determinism? There is, says Gary Whittenberger, in this evocative article in response to a debate in the pages of…

Shermer and Berent discuss: nature/nurture genes/environment biology/culture • language and innate knowledge • what babies are born knowing • how people reason about human nature • dualism • essentialism • theory of mind • the nature of the self • innate beliefs in the soul and afterlife • free will and determinism • how people think about mental illness and disorders • how one’s theory of human nature effects one’s attitudes about nearly everything.

Shermer and Gregg discuss: • intelligence • stupidity • dolphins • artificial intelligence • language • rationality • moral systems • comparative thanatology • “causal inference” vs. “learned associations” • humans as “why specialists” • death awareness • why narwhals do not commit genocide • “prognostic myopia” • our “shortsighted farsightedness” as “an extinction-level threat to humanity” • consciousness and sophisticated consciousness: animals and humans • free will • determinism • pleasure vs. happiness vs. purposefulness.

Shermer and Palmer discuss: doubt and skepticism • when doubt slides into denial • uncertainty as a measurement problem vs. inherent in natural systems • contingency and necessity, randomness and law • the butterfly effect • the geometry of chaos • quantum uncertainty • weather forecasting • climate change • pandemics • economic recessions • human decision making and creativity • free will • consciousness, and God.

Shermer and Marcus discuss: why AI chatbot LaMDA is not sentient • “mind”, “thinking”, and “consciousness”, and how do molecules and matter give rise to such nonmaterial processes • the hard problem of consciousness • the self and other minds • How would we know if an AI system was sentient? • Can AI systems be conscious? • free will, determinism, compatibilism, and panpsychism • language • Can we have an inner life without language? • How rational or irrational…

Shermer and Azarian discuss: laws of thermodynamics and directionality • how complexity formed after the Big Bang • laws of nature: discovered or created or both? • Stephen Jay Gould and contingency vs. necessitating laws of nature • convergent evolution and directionality in evolution • the left wall of simplicity • leading theories for the origin of life • complexity theory and emergence • consciousness, the self, and other minds • free will, determinism, compatibilism, panpsychism • Is there purpose…

Shermer and Seth discuss: consciousness • controlled hallucinations • the self and other minds • Where does consciousness go during general anaesthesia? After death? • Are we living in a simulation that itself is inside a simulation? • Does Deep Blue know that it beat the great Gary Kasparov in chess? • Does Watson know that it beat the great Ken Jennings in Jeopardy!? • Is Data on Star Trek sentient, conscious, and with feelings? • Can AI systems be…

Michael Shermer speaks with psychologist and behavioral scientist, Stuart Vyse, about aspects of human nature that are not altogether rational but, nonetheless, help us achieve our social and personal goals. In his book, and in this conversation, Vyse presents an accessible exploration of the psychological concepts behind useful delusions, fleshing out how delusional thinking may play a role in love and relationships, illness and loss, and personality and behavior.

Michael Shermer speaks with computational neuroscientist, Ogi Ogas, about his unified account of the mind that explains how consciousness, language, self-awareness, and civilization arose incrementally out of chaos, and how leading cities and nation-states are developing “superminds,” and perhaps planting the seeds for even higher forms of consciousness.
NEXT →