human behavior

Shermer and Hood discuss: psychedelic drugs • defining the “good life” or “happiness” • measuring emotions • happiness as social contagion • eudaimonia (the pursuit of meaning) versus hedonism (the pursuit of pleasure) • genetics and heritability • cultural components • WEIRD people • The Big Five (OCEAN) • marriage and health • exercise and stress reduction • what the ancient Greeks got right about living the good life • how failure may actually be a key to more happiness…

Our society is obsessed with achievement. Young people are pushed toward the next test or the “best” grammar school, high school, or college they can get into. Adults push themselves toward the highest-paying, most prestigious jobs, seeking promotions and public recognition. As Adam Gopnik points out, the result is not so much a rat race as a rat maze, with no way out. Except one: to choose accomplishment over achievement. Gopnik provides timeless wisdom against the grain.
In the controversies surrounding campaigns to ban books from school libraries and publishers’ new policy of removing offensive words from classic books, most commenters focus on the nature of the books’ content and whether it’s appropriate for children of a certain age. In contrast, this essay focuses on the nature of stories and how concerned parents should think about them in the context of their children’s moral and social development.

Shermer and Sapolsky discuss: free will, determinism, compatibilism, libertarian free will • Christian List’s 3 related capacities for free will • how what people believe about free will and determinism influences their behaviors • the three horsemen of determinism: (1) reductionism (2) predetermination; (3) epiphenomenalism • dualism • punishment • retributive vs. restorative justice •Is the self an illusion? • game theory evolution of punishment • luck • and meaning (or lack thereof).

Shermer and Segal discuss: her historical interest in twins research and behavior genetics • the many different types of twins and family arrangements • twins separated accidentally • twins separated intentionally • twins reunited • a brief history of twins research • Josef Mengele • Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart • the gay fathers and twin sons story • immigration and naturalization law related to IVF, twins, gay couples, etc. • abortion • eugenics and the Nobel Prize sperm…
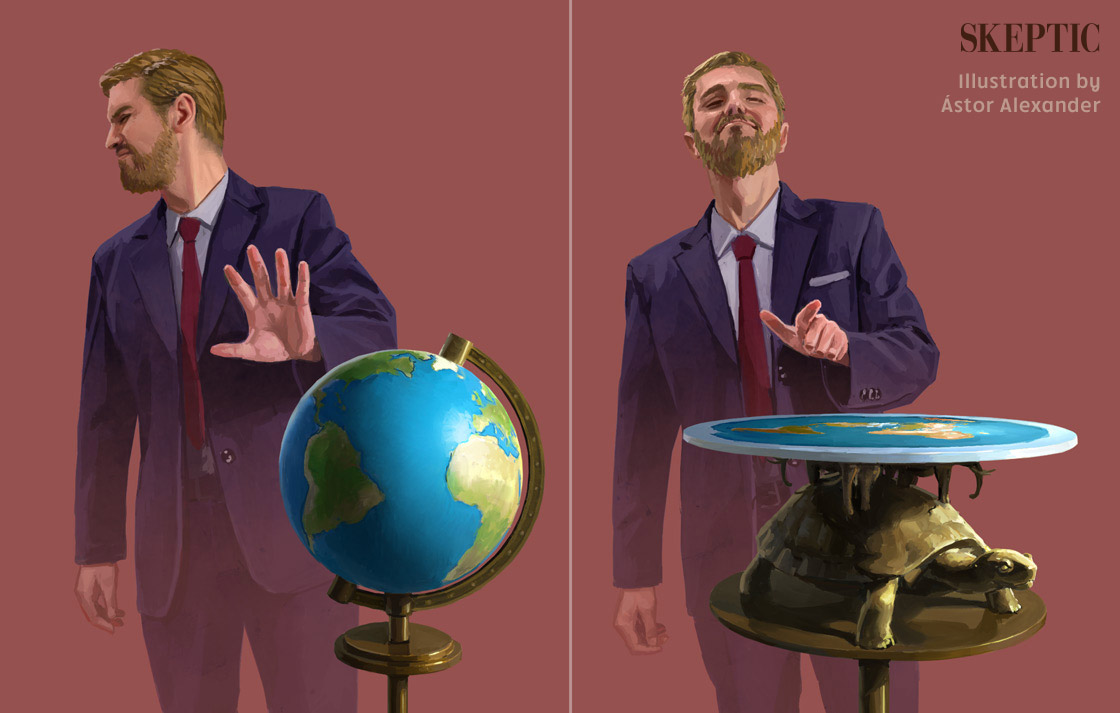

In this review of investigative journalist Kelly Weill’s important book on the flat Earth movement, the people involved, and their psychology, readers will discover that the flat Earth movement contains a great diversity of beliefs. As an example, an obvious question is why don’t we find an edge? Well, some say, there is an edge—it’s the Antarctic which forms an ice wall around the flat Earth to keep the oceans from spilling over the edge. But regular people can’t go…

There is probably no other scientific discipline in which fads come and go so quickly, and with so much hype, as psychology. In his Quick Fix, Jesse Singal discusses eight different psychological ideas that have been promoted as quick fixes for different social problems. He refers to these as “half-baked” ideas—ideas that may not be 100 percent bunk but which are severely overhyped. This review of Singal’s book discusses the many different flawed studies that derailed psychology for years.

In recent years a number of books written by women in their 30s reflect on their sexual histories in their 20s in a regretful way, deciding that the type of feminism that liberated women to have sex like men — carefree and commitment-free with a variety of partners and with no consequences — is perhaps not the best strategy inasmuch as women and men differ in their sexual psychology. In this article psychologist Carol Tavris evaluates this claim and how…

Shermer and Pigluicci discuss: his journey from Rome to New York • evolutionary biology • stoic philosophy • can there be a science of meaning and morality? • ultimate questions • desire, action, depression, suicide, anger, anxiety, love, and friendship • practical spiritual exercises • how to react to situations • teaching virtue to politicians • philosophy and politics • character and leadership • the nature of evil.

Shermer and Hassan discuss: types of cults, their characteristics • cult leader profiles • the influence continuum • mind control • brainwashing • Project MK-ULTRA • Scientology • NXIVM • strip search hoax • social media mind control • neuroscience of mind control • authoritarian mindset • Trump’s mind-control techniques • breaking free of cults.

The philosophical problem of free will and determinism—how can humans have any sort of volition in a world determined by the laws of nature?—has troubled thinkers since the time of the ancient Greeks, and here in the 21st century there is still no consensus among thinkers on a solution to the problem. Can science help? Is there some way to test determinism? There is, says Gary Whittenberger, in this evocative article in response to a debate in the pages of…

According to the standard model of evolutionary psychology females tend to be sexually coy, discriminating, and risk averse while males are sexually assertive, indiscriminate, and risk taking. Not so fast, says Carol Tavris in this skeptical look at the standard model, as context and species also matters in how we analyze behavior, especially sexuality.

Shermer and Cobb discuss: objections to genetic engineering (political, religious, cultural) • selective breeding • recombinant DNA • the ethics of genetics • patenting life • gene therapy • gene editing • CRISPR • literature and films on the dangers of genetic engineering • bioweapons • 3 Laws of Behavior Genetics and what people fear about it.

Shermer and Cooke discuss: the definition of male and female across the animal kingdom • male bias in the history of science • genes involved in sex determination and how they work • sexual selection • adaptationism vs. non-adaptationism • Why do women have orgasms? • why female animals are just as promiscuous, competitive, aggressive, dominant and dynamic as males • what humans can learn from non-human animals • maternal/paternal instincts • patriarchy/matriarchy across the animal kingdom • why the sexes…

Moshe Hoffman is a research scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology whose research focuses on using game theory and models of learning. Erez Yoeli is a research scientist at MIT’s Sloan School of Management, whose research focuses on altruism: understanding how it works and how to promote it.

Michael Shermer and Jesse Singal discuss: how social scientists determine causality • cognitive priming • The Malcolm Gladwell-effect • self-help movements • power posing • positive psychology • Implicit Association Test • racism, gender, class, misogyny, bigotry • replication crisis • choice architecture • I.Q. • free will and determinism • nature/nurture and how lives turn out • abortion • and U.S. foreign policy.
Michael Shermer speaks with Jesse Singal about this new book: Why Fad Psychology Can’t Cure Our Social Ills.
In this letter to Bert Hölldobler, following up on his defense of his long-time colleague E. O. Wilson, who has been falsely accused of racism and knowingly promoting race science, Mel Konner, who also knew and worked with Wilson, reinforces the point that Wilson’s defense of Philippe Rushton was done out of concerns about academic freedom; in fact, Konner notes that there are other reasons for critiquing Wilson, primarily for his ultimate rejection of kin selection — one of the…
Mel Konner, in response to Bert Hölldobler’s defense of E. O. Wilson, reinforces the point that Wilson’s defense of Philippe Rushton was done out of concerns about academic freedom; PLUS: Michael Shermer speaks with Oliver Stone about Ukraine, Putin, and the military-industrial complex.
Mark W. Moffett remind us that breakthroughs in science often come about by exploring points of similarity between things that are normally seen as very different. PLUS: Michael Shermer speaks with quantum physicist, Jim Al-Khalili, who reveals how 8 lessons from the heart of science can help us all get the most out of our lives. PLUS: In SRC Report PCIS-005, we take a look at Conspiracy Theory Endorsement by Generation.
NEXT →