influence

Shermer, Simons, and Chabris discuss: • How rational vs. irrational are humans? (Daniel Kahneman vs. Gerd Gingerenzer) • Truth Default Theory, or Truth Bias • deception vs. deception detection • social proof and the influence of others on our beliefs • cults • Bernie Madoff • Harvey Weinstein • Elizabeth Holmes and Theranos • Nigerian spam scam • cheating in chess • habits of thought that can be exploited • information hooks we find especially enticing instead of triggering skepticism…

Shermer and Sheldon discuss: definitions of free will, determinism, compatibilism, libertarian free will • dualism • reductionism, materialism, predetermination, and epiphenomenalism • Christian List’s three capacities for free will • AI, Star Trek’s Data, sentience and consciousness, ChatGPT, GPT-4 • how what people believe about free will and determinism influences their behaviors • the case for hard determinism • brain injuries, tumors, addictions, and other “determiners” of behavior • emergence • symbolic self • System 1 vs. System 2 thinking • Experiencing Self vs.…

In their debate on free will, Doyle and Whittenberger present, explain, and defend contrasting, inconsistent, and in some ways contradictory models of human decision making. Whittenberger believes that the free will model is far inferior to the hard determinism model in so many ways, including conceptual clarity, the reasonableness of premises, and evidential support. Read Whittenberger’s response to Doyle.

Shermer and Fridland discuss: Okay, Boomer language • accents • ChatGPT • gender pronouns • gender differences in language use • forensic language analysis • evolution of language • why children learn language naturally but must be taught to read and write • literature, film, and TV’s influence on language use • cancel culture and taboo language • language and identity politics • y’all, contractions, and other language shortcuts • tracking human migrations by language, and vice versa • Fargo,…
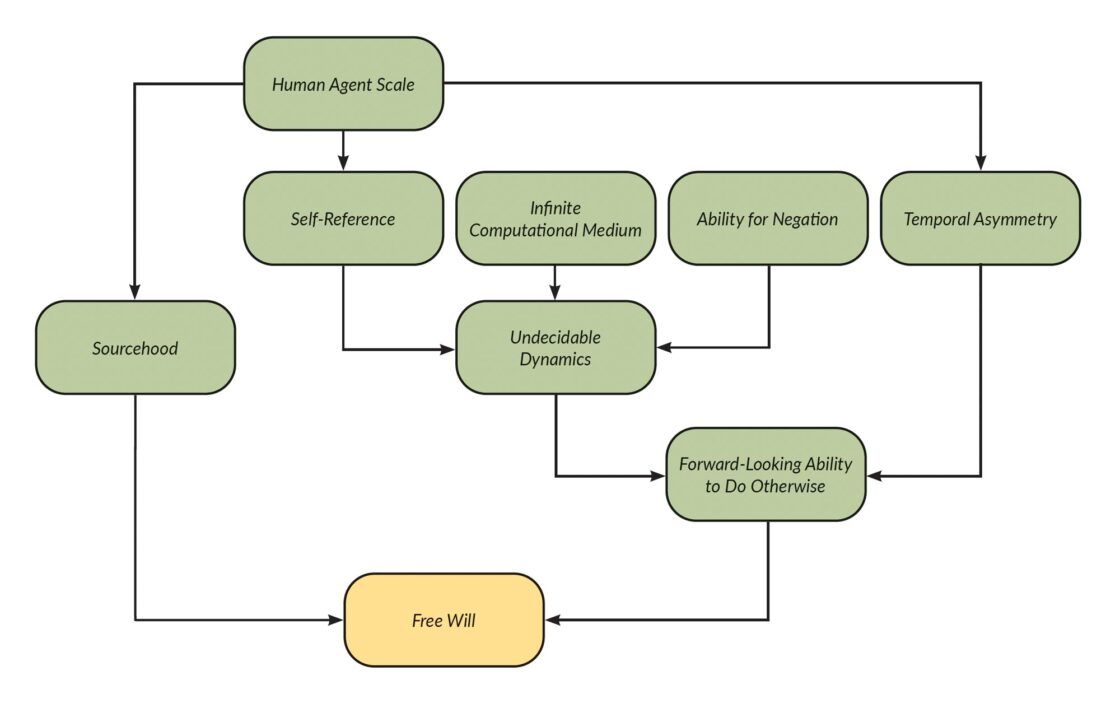
Are we really free? The question “Could I have done otherwise?” is central to the issue of free will. But because choices are forward-looking, at the time of choice there is not yet any action to do otherwise. The question makes more sense when aimed at the future: “Can I do something fundamentally unpredictable?” The answer is yes! Humans possess properties that make us capable of undecidable dynamics, meaning we are fundamentally unpredictable, and so we do have free will.

Shermer and Hassan discuss: types of cults, their characteristics • cult leader profiles • the influence continuum • mind control • brainwashing • Project MK-ULTRA • Scientology • NXIVM • strip search hoax • social media mind control • neuroscience of mind control • authoritarian mindset • Trump’s mind-control techniques • breaking free of cults.

The philosophical problem of free will and determinism—how can humans have any sort of volition in a world determined by the laws of nature?—has troubled thinkers since the time of the ancient Greeks, and here in the 21st century there is still no consensus among thinkers on a solution to the problem. Can science help? Is there some way to test determinism? There is, says Gary Whittenberger, in this evocative article in response to a debate in the pages of…

Shermer and Kashdan discuss: how he became an insubordinate rebel in his unusual young life • the effects of a fatherless home on children • the influence of role models • how civil rights movements make progress • the adversarial court system • how juries should think • racialization in America • viewpoint diversity • resisting complacency • the value of non-conformity • influencing the majority (when in the minority) • how to build alliances • how to champion ideas…

Shermer and Ashton discuss: what it’s like advising Google and Buckingham Palace on how to communicate • what makes writing appealing and effective • how to write better emails and social media posts • why the messages we write often backfire • why emails so often make us angry • What makes Donald Trump such a powerful communicator that he can seemingly hypnotize tens of millions of people and dictate entire news cycles with a single statement? • when you…

In episode 211, Michael Shermer speaks with Ashley Rindsberg about his book The Gray Lady Winked in which he pulls back the curtain to reveal an eye-opening, often shocking, look at the New York Times’s greatest journalistic failures, so devastating they changed the course of history.
In episode 211, Michael Shermer speaks with Ashley Rindsberg about his book The Gray Lady Winked in which he pulls back the curtain to reveal an eye-opening, often shocking, look at the New York Times’s greatest journalistic failures, so devastating they changed the course of history.

A review by Dr. Harriet Hall of Abigail Shrier’s 2020 book Irreversible Damage: The Transgender Craze Seducing Our Daughters was originally published on Science-Based Medicine’s website and later removed and put under review by SBM’s Editors “due to concerns expressed over its scientific accuracy and completeness.” Skeptic is publishing here because, if skepticism means anything, there are no sacred cows, no political sensitivities of topics to prohibit open discussion and review, no censorship of ideas that don’t toe a political…

In episode 187, Michael speaks with Robert Cialdini — New York Times bestselling author of Pre-Suasion and the seminal expert in the fields of influence and persuasion — about the psychology of why people say yes and how to apply these insights ethically in business and everyday settings.
In episode 187, Michael speaks with Robert Cialdini — New York Times bestselling author of Pre-Suasion and the seminal expert in the fields of influence and persuasion — about the psychology of why people say yes and how to apply these insights ethically in business and everyday settings. PLUS, the newest issue of Skeptic magazine (26.2: Drug Trips & Reality) is now available in print and digital formats.
In Science Salon # 35, Michael Shermer talks with neuroscientist Tali Sharot about her new book The Influential Mind in which she takes readers on a thrilling exploration of the nature of influence.

Cognitive neuroscientist Tali Sharot takes us on a thrilling exploration of the nature of influence. She and Shermer discuss how we can influence, for example, climate deniers to accept climate science, anti-vaxxers to accept vaccines, and creationists to accept evolution. It turns out, for example, that many of our instincts—from relying on facts and figures to shape opinions, to insisting others are wrong or attempting to exert control—are ineffective, because they are incompatible with how people’s minds operate.
What will people look like centuries from now? How will they act? What race and gender roles that we take as natural today will be the same or different in the far future? In this insightful look into the future Carol Tavris, one of today’s most prominent social scientists and psychologists, considers how blinded we all are to the influences of the times in which we live.