causality

Shermer and Klaas discuss: contingency and necessity/convergence • chance and randomness • complexity and chaos theory • Jorge Luis Borges “The Garden of Forking Paths” • self-organized criticality • limits of probability • frequency- vs. belief-type probability • ceteris paribus, or “all else being equal” • economic forecasting • Holy Grail of Causality • Hard Problem of Social Research • Special Order 191 and the turning point of the Civil War • Hitler, Nazi rise to power in Germany, World…

Shermer and Greger discuss: • why we age and die • lifespan, vs. healthspan • longevity escape velocity • how to determine causality in aging science • nutrition fads • the anti-aging industry • Centenarians Diet • Mediterranean Diet • Okinawan Diet • Red, White, and Blue Zones • plant-based eating • exercise, sleep, stress • the Anti-Aging 8 • cholesterol and statins • vaccines • brain supplements • UV protection • alcohol • Alzheimer’s • social ties, friendships, and…
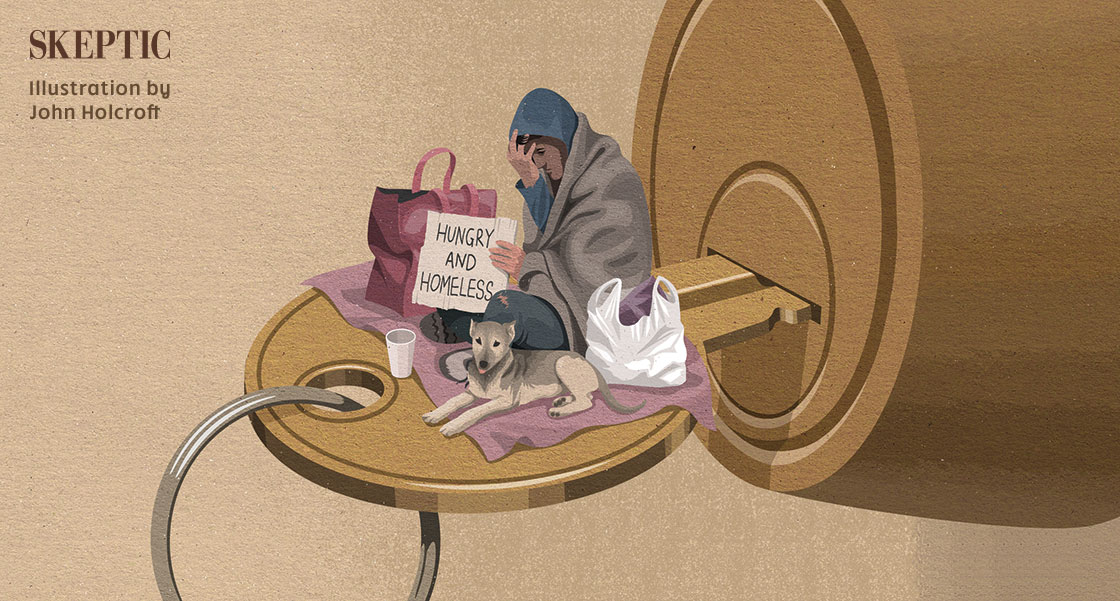

The reason why America has so much homelessness is simple: our big cities have extraordinary high housing costs, and a growing number of city dwellers can’t afford even the most basic accommodations. But if a lack of cheap housing is the cause of mass homelessness, then its solution is equally simple. Overwhelming evidence shows that building more homes will drive housing costs down to manageable levels, and getting unhoused people into housing — along with supportive services, as needed —…

In their debate on free will, Doyle and Whittenberger present, explain, and defend contrasting, inconsistent, and in some ways contradictory models of human decision making. Whittenberger believes that the free will model is far inferior to the hard determinism model in so many ways, including conceptual clarity, the reasonableness of premises, and evidential support. Read Whittenberger’s response to Doyle.
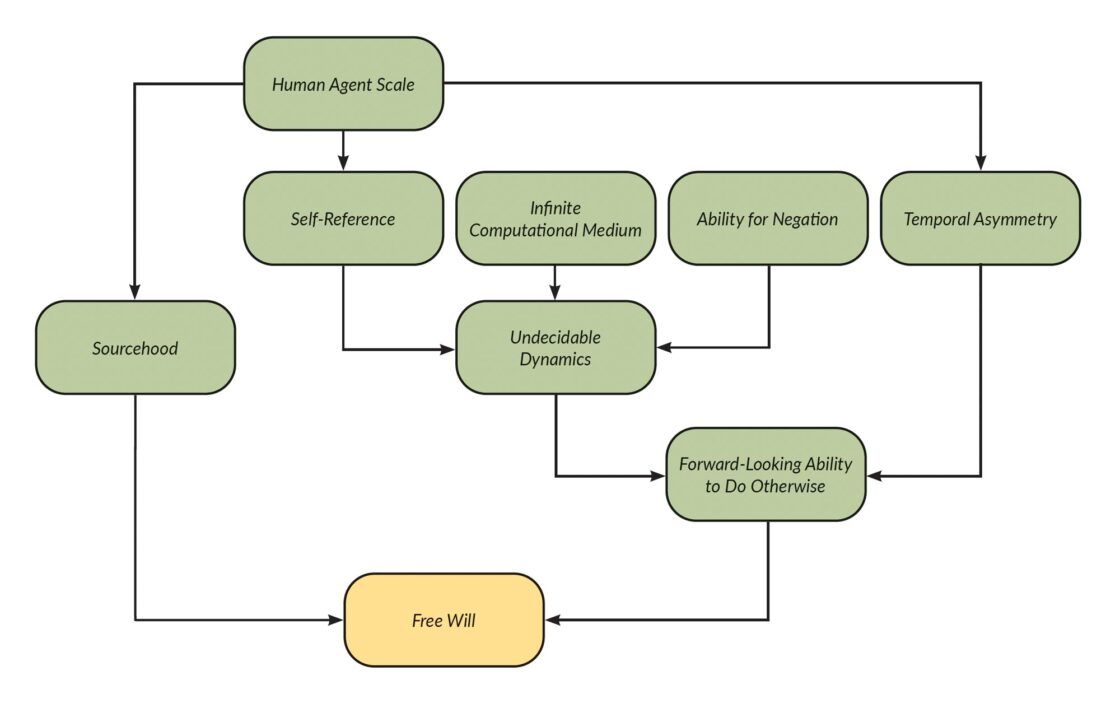
Are we really free? The question “Could I have done otherwise?” is central to the issue of free will. But because choices are forward-looking, at the time of choice there is not yet any action to do otherwise. The question makes more sense when aimed at the future: “Can I do something fundamentally unpredictable?” The answer is yes! Humans possess properties that make us capable of undecidable dynamics, meaning we are fundamentally unpredictable, and so we do have free will.

The philosophical problem of free will and determinism—how can humans have any sort of volition in a world determined by the laws of nature?—has troubled thinkers since the time of the ancient Greeks, and here in the 21st century there is still no consensus among thinkers on a solution to the problem. Can science help? Is there some way to test determinism? There is, says Gary Whittenberger, in this evocative article in response to a debate in the pages of…

With the widespread use of cell phone towers and internet technology, concerns have arisen over health effects of wireless energy, most notably with the recent introduction of Fifth Generation (5G) wireless network technology. Public health expert Raymond Barglow reviews the epidemiological data and science behind these concerns and shows that there is, in fact, nothing to worry about.

If you give Christians a choice between Jesus and Darwin by telling them that the theory of evolution means you have to be an atheist, they’re going to pick Jesus every time. In this article, Larry Arnhart argues that Christians should accept the theory of evolution not only because it’s true but also that it does not mean they have to give up their religion.

In episode 189, Michael speaks with Nobel Prize winning psychologist and economist Daniel Kahneman about the detrimental effects of noise and what we can do to reduce both noise and bias, and make better decisions in: medicine, law, economic forecasting, forensic science, bail, child protection, strategy, performance reviews, and personnel selection.
In episode 189, Michael speaks with Nobel Prize winning psychologist and economist Daniel Kahneman about the detrimental effects of noise and what we can do to reduce both noise and bias, and make better decisions in: medicine, law, economic forecasting, forensic science, bail, child protection, strategy, performance reviews, and personnel selection. PLUS: We present a review by Dr. Harriet Hall of Abigail Shrier’s 2020 book Irreversible Damage: The Transgender Craze Seducing Our Daughters was originally published on Science-Based Medicine’s website…

Shermer and Christakis discuss: the replication crisis in social science and medicine • determining causality: how we know smoking causes cancer and HIV causes AIDS, but vaccines do not cause autism and cell phones do not cause cancer • randomized controlled trials and why they can’t be done to answer many medical questions • natural experiments and the comparative method of testing hypotheses (e.g., comparing different countries differing responses to Covid-19) • the hindsight bias and the curse of knowledge…
In Science Salon podcast # 135, Michael Shermer speaks with Paul Halpern about his new book Synchronicity: The Epic Quest to Understand the Quantum Nature of Cause and Effect.

Does the universe have a speed limit? If not, some effects could happen at the same instant as the actions that caused them — and some effects, ludicrously, might even happen before their causes. Paul Halpern is a professor of physics at the University of the Sciences in Philadelphia and the author of sixteen popular science books.